Introduction
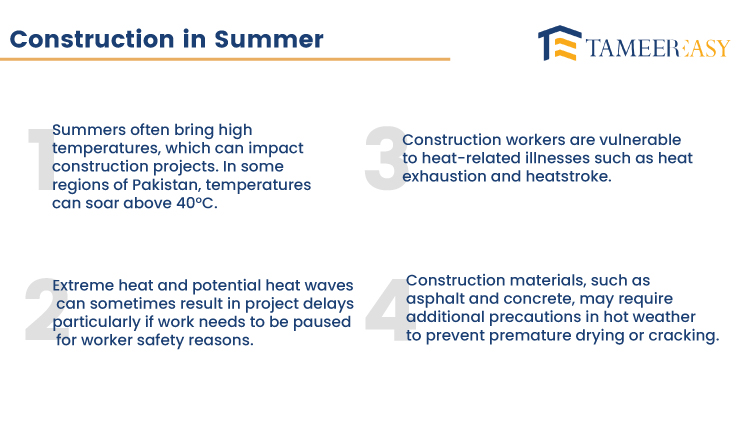
The building industry has significant difficulties during Pakistan’s summer because of the country’s extreme heat and humidity. Some places have temperatures above 40°C (104°F), challenging construction projects that require careful design and adaptation.
This article examines the effects of high temperatures and humidity on building projects in Pakistan, emphasising the steps used to deal with these conditions, guarantee worker safety, keep projects on schedule, and reduce potential dangers.
Here are some of the top issues and their solutions:
1). Recognising Heat and Humidity
During the summer, Pakistan endures sweltering heat and high humidity levels. Inconvenient working conditions, a higher risk of heat-related illnesses, and significant material damage can all result from the combination of heat and humidity.
Construction industry professionals must comprehend how these elements affect them and put the right plans in place to lessen their consequences.
2). Precautions for Worker Safety and Health
During summer building projects, the safety of construction workers is of the utmost importance. Employers must prioritise steps like offering enough shade, drinking, and rest intervals to assure their safety.
Workers should be given personal protection equipment (PPE), including wide-brimmed hats, light clothing, and sunscreen to protect them from the sun’s harmful rays. Programs for teaching people how to identify and treat illnesses brought on by excessive heat are also crucial.
3). Modifying Construction Techniques
Construction techniques and procedures must be modified to endure excessive heat and humidity. Materials like asphalt and concrete require extra care because they can dry too rapidly or cure incorrectly in hot weather.
These difficulties can be lessened with shade, misting, and temperature-lowering additives. Reduce exposure to excessive heat by scheduling construction work at cooler hours or choosing night shifts.
4). Effective Management of Water
In Pakistan, where there is a severe water shortage, summer construction projects necessitate careful water management. This priceless resource can be preserved by using effective irrigation methods, reusing water, and minimising waste.
Water usage in landscaping and green spaces around building sites can be decreased using cutting-edge methods like hydroseeding and hydroponics.
5). Solutions for Energy Efficiency and Cooling
Energy-efficient building design and construction become essential to reduce cooling needs during the summer. A comfortable indoor climate can be achieved using passive cooling strategies, including natural ventilation and shading, insulation, energy-efficient materials, and materials.
Incorporating renewable energy sources and energy-efficient air conditioning systems can also lessen the environmental impact and long-term energy expenses.
6). Collaboration and Participant Involvement
Collaboration between contractors, architects, engineers, and stakeholders is necessary for successful summer construction projects. Early participation from all parties aids in planning efficiently, spotting potential problems, and identifying workable solutions.
Regular communication, feedback loops, and flexible response to changing conditions influence successful project outcomes.
7). Scheduling and early planning
For construction work during the summer, careful planning and timing are essential. Construction activities can be strategically scheduled to reduce exposure to the warmest hours of the day by starting projects earlier or altering timeframes.
This enables better resource management, increased labour efficiency, and decreased dangers of excessive heat to one’s health.
8). Environment-Related Issues
Environmental concerns are important during summer construction projects. Measures to reduce air pollution and minimise the effects of dry conditions include water spraying on building sites. We can use erosion control techniques and stormwater management systems to stop runoff and safeguard nearby water bodies.
Environmental conservation efforts aided by sustainable practices, which include minimising waste production and employing eco-friendly building materials, are the best solution.
9). Evaluation and Monitoring
Throughout the summer, consistent monitoring and evaluation of building projects enable the identification of potential dangers, timely resolution of issues, and confirmation of adherence to safety requirements. The efficiency of applied heat mitigation measures should be assessed by regular inspections by site supervisors and safety authorities, who should also monitor worker conditions and hydration levels.
Conclusion
Due to the intense heat and humidity, summer construction in Pakistan provides considerable hurdles. The construction sector may successfully adjust to these conditions by prioritising worker safety, applying adaption techniques, smart water management, energy-efficient designs, and encouraging teamwork.
Promptly adopting necessary precautions ensures project completion while preserving worker safety and reducing environmental effects.








